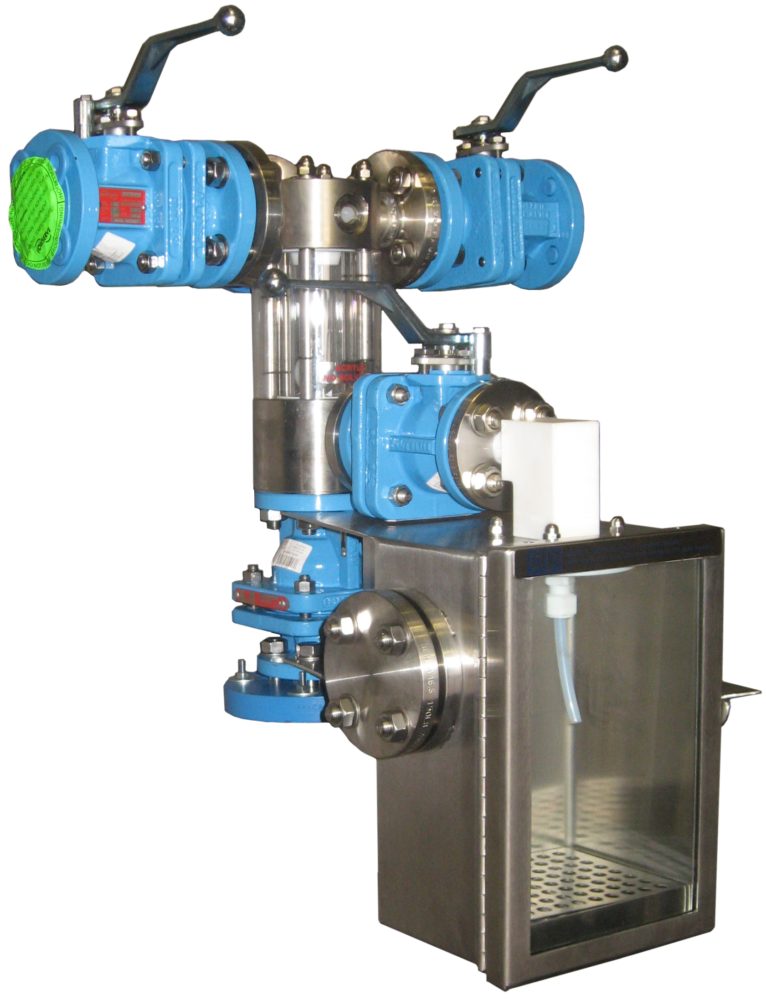
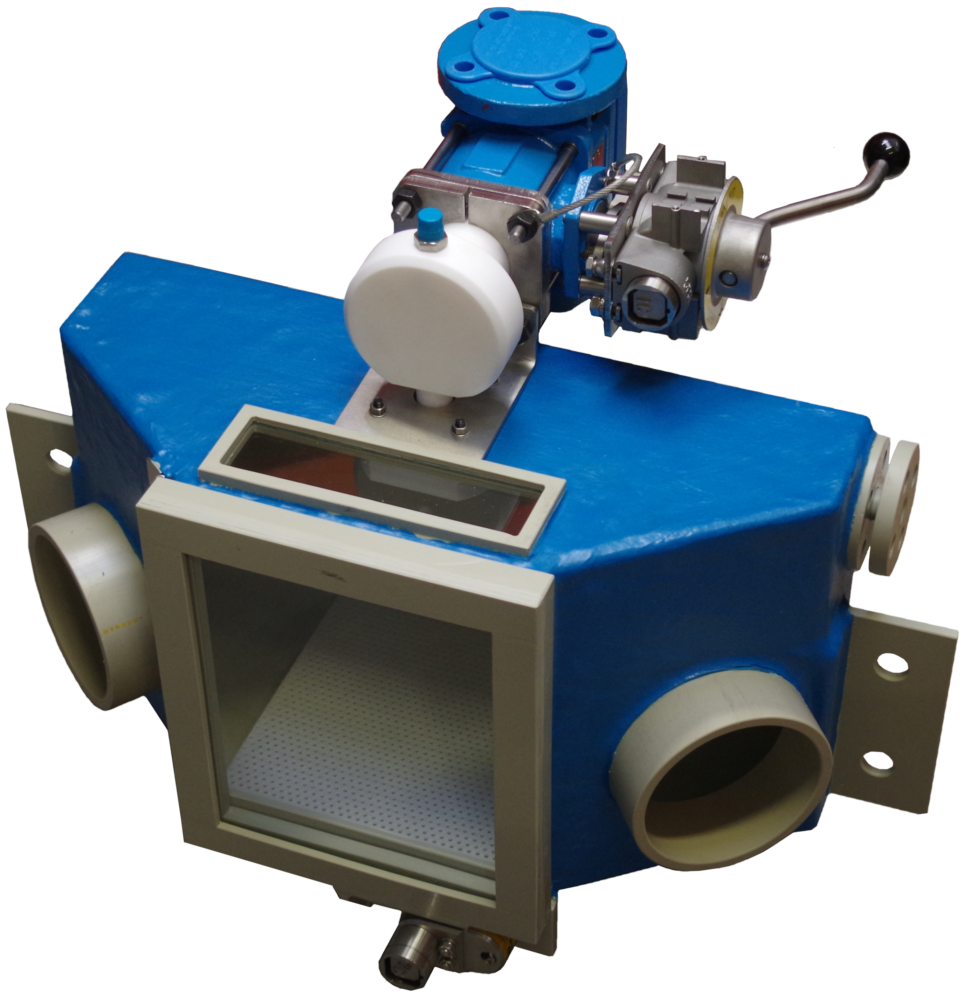
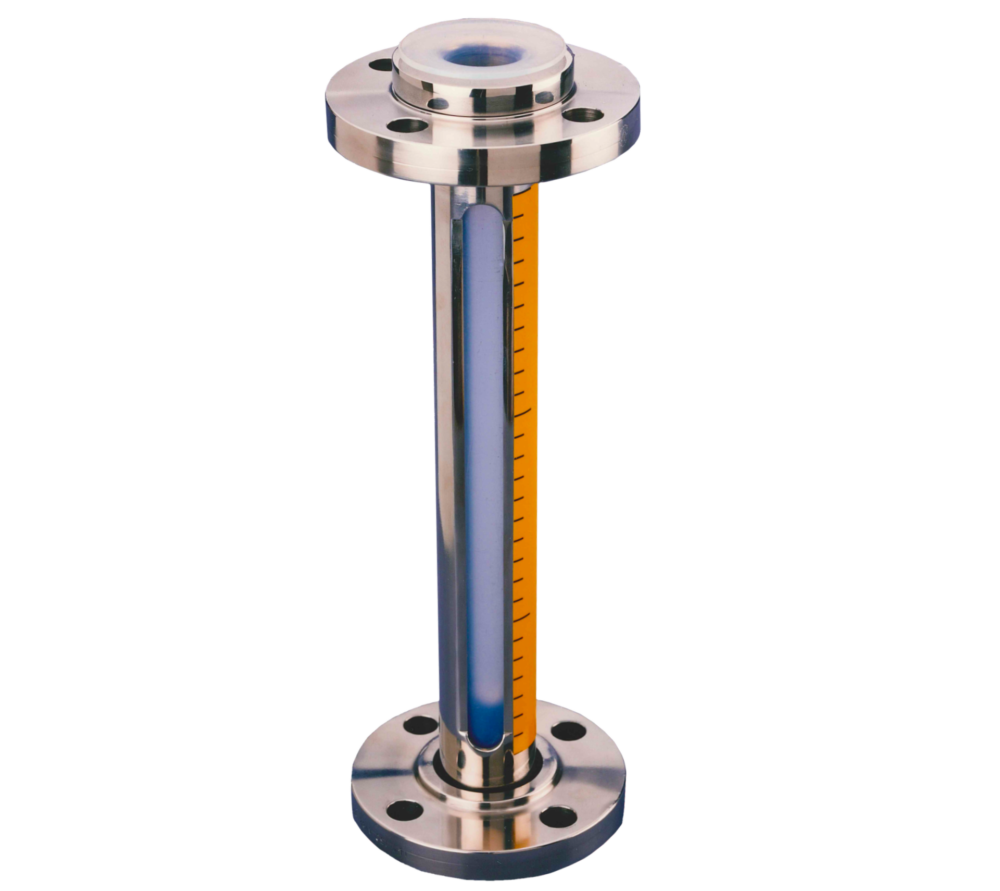
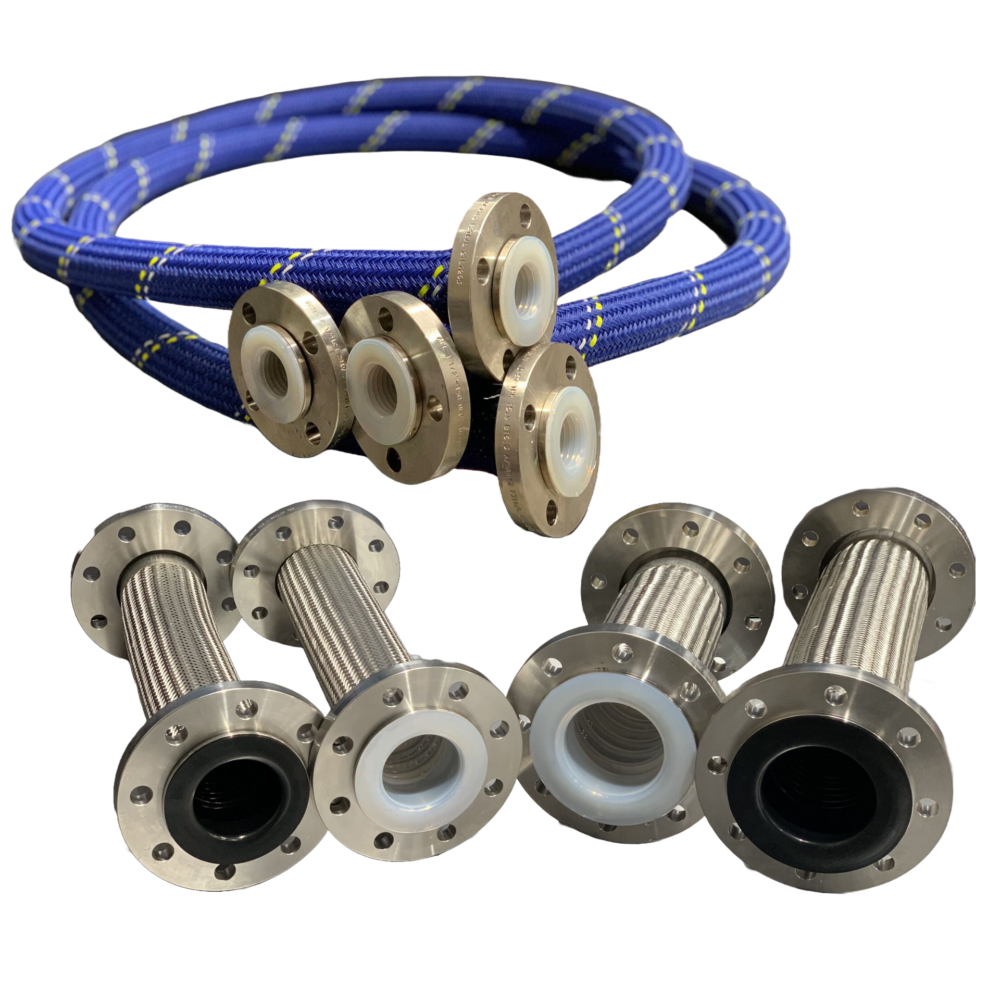
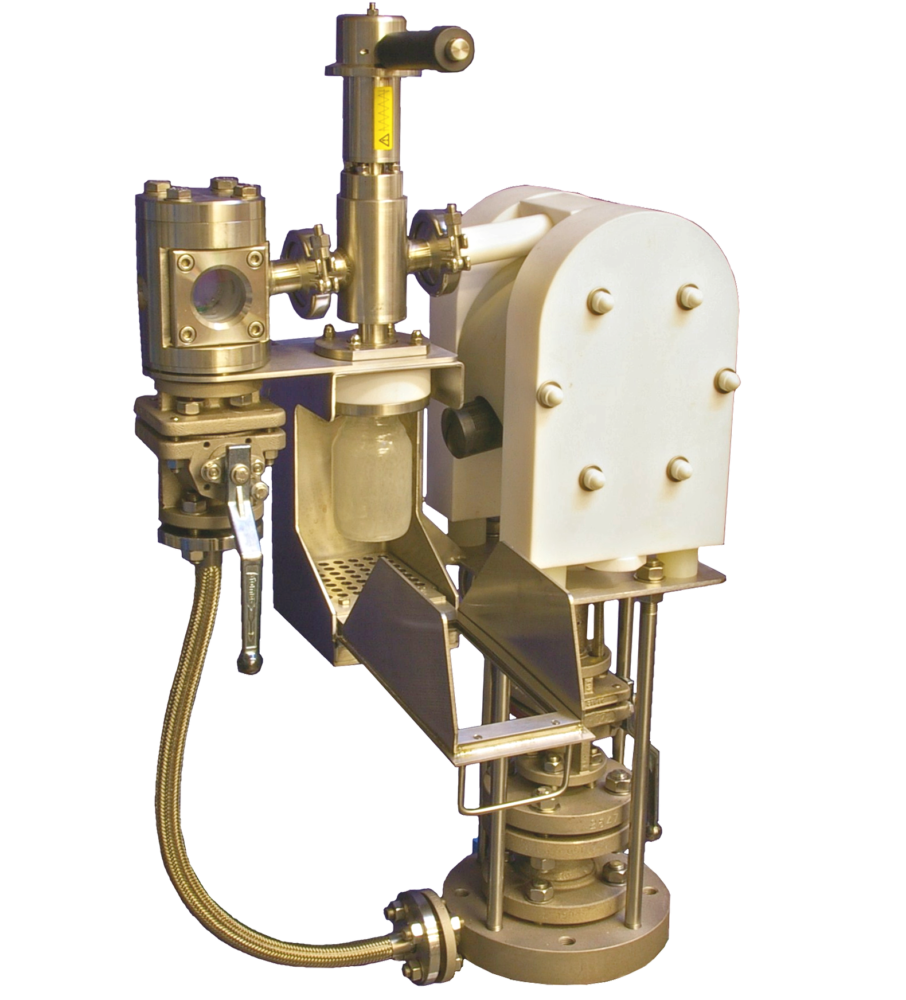
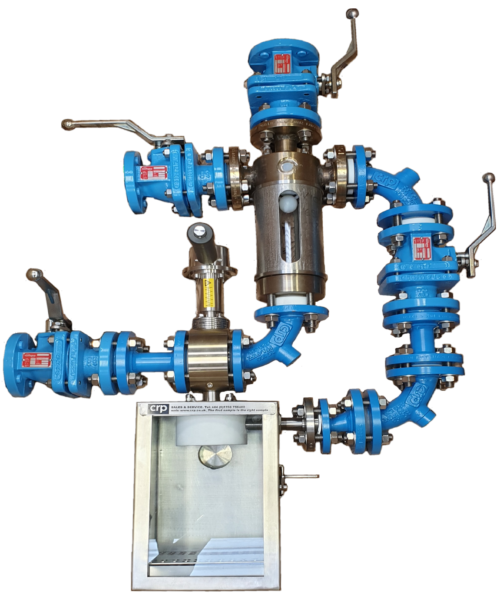
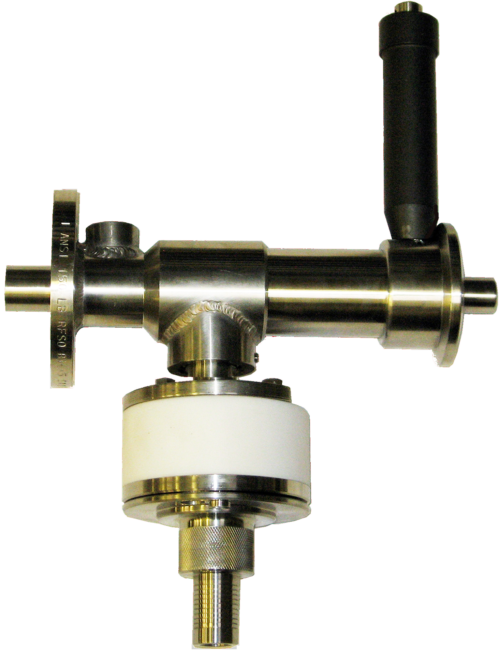
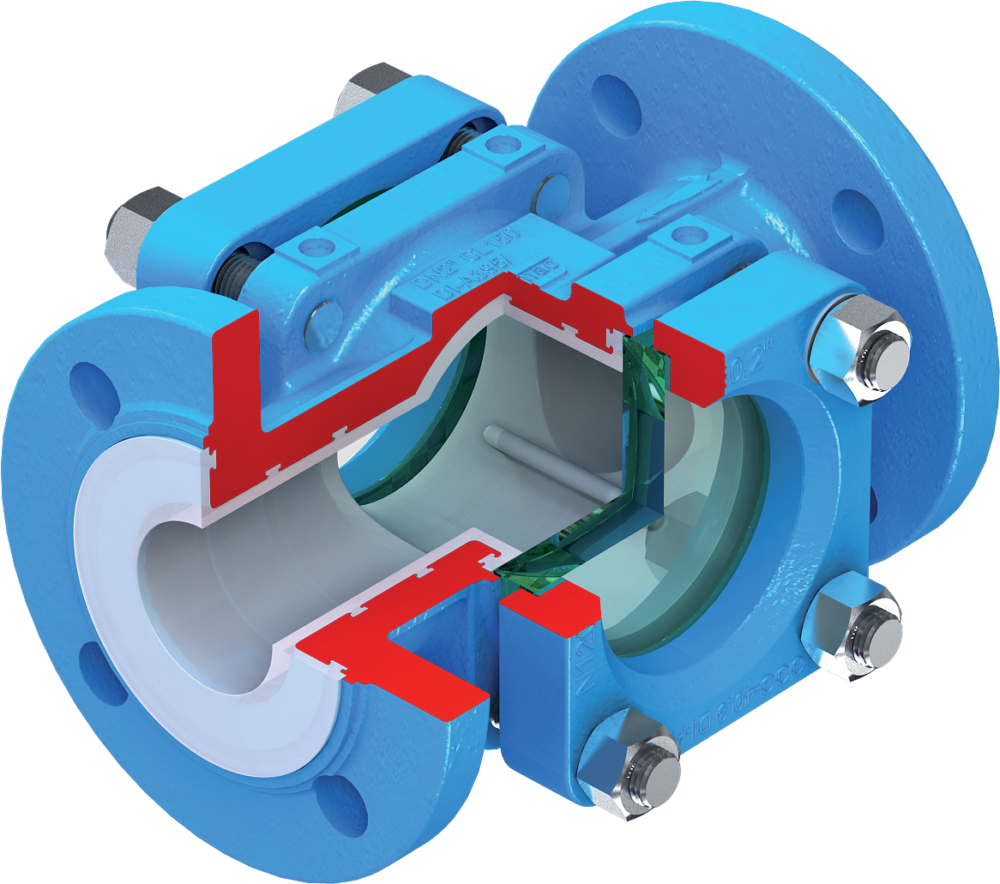
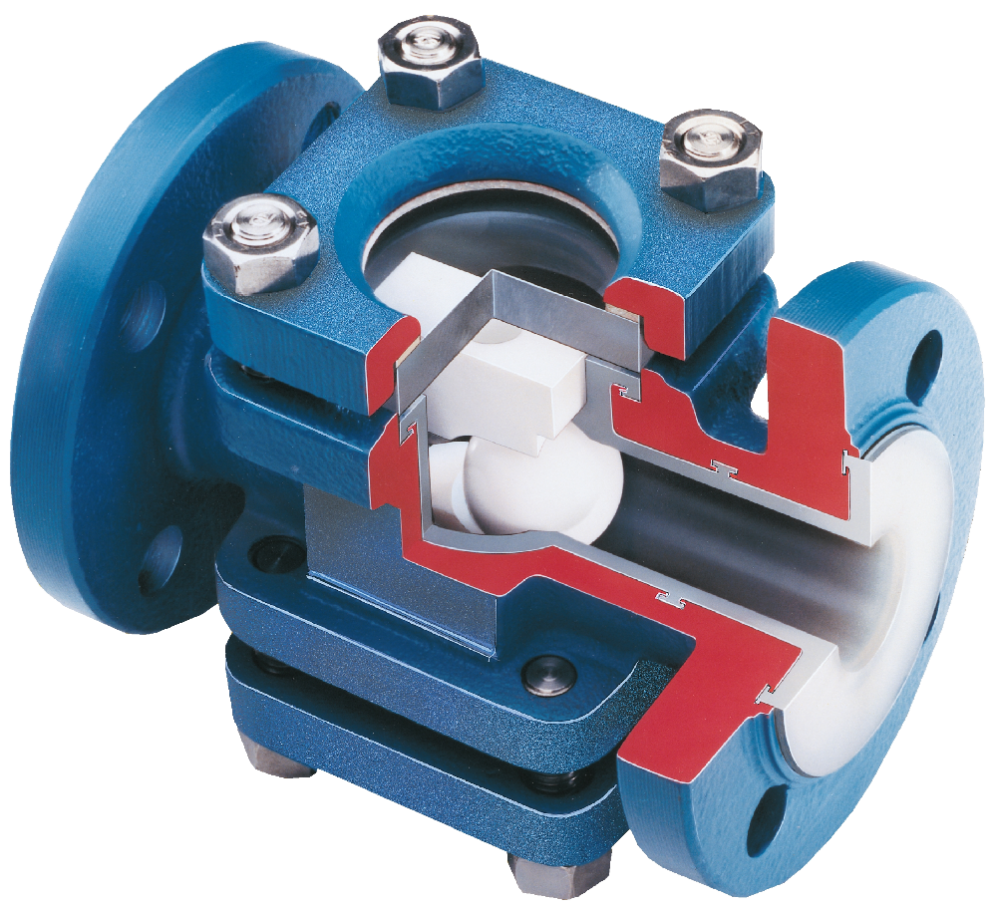
Typical operation of a non-recirculating sampler
Typical operation of a non-recirculating sampling system
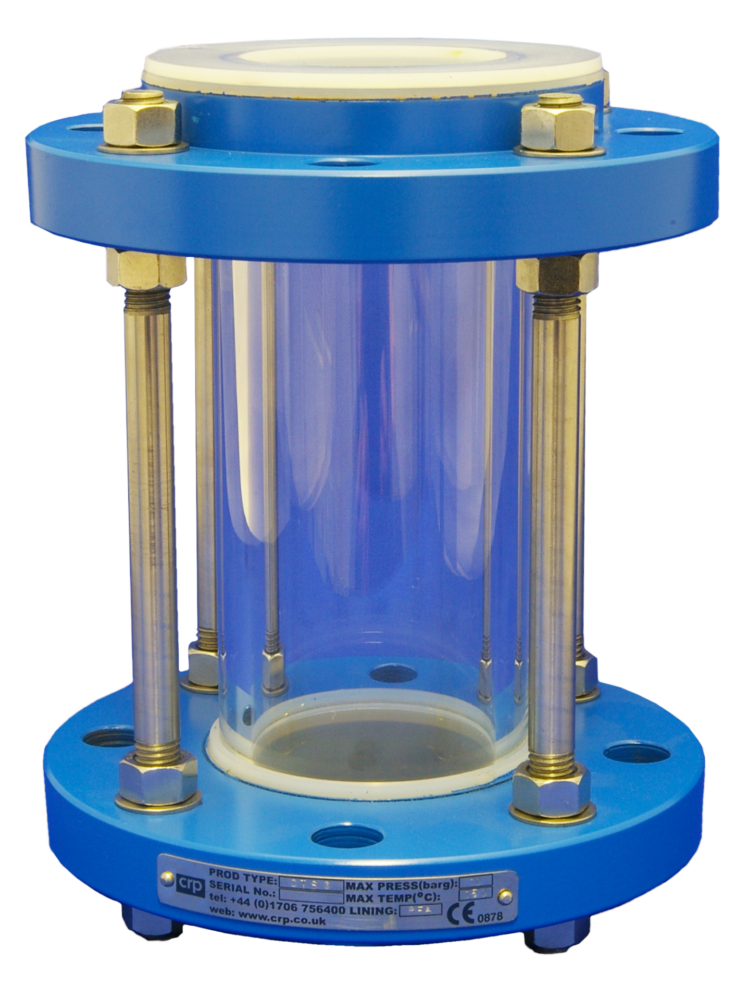
1. First Purge
Introduce nitrogen into the sampling system and open the vessel isolation valve. The nitrogen flows through the sight glass chamber and down the bore of the dip pipe blowing clear any residue from the system and the dip pipe ready to take a fresh representative sample.
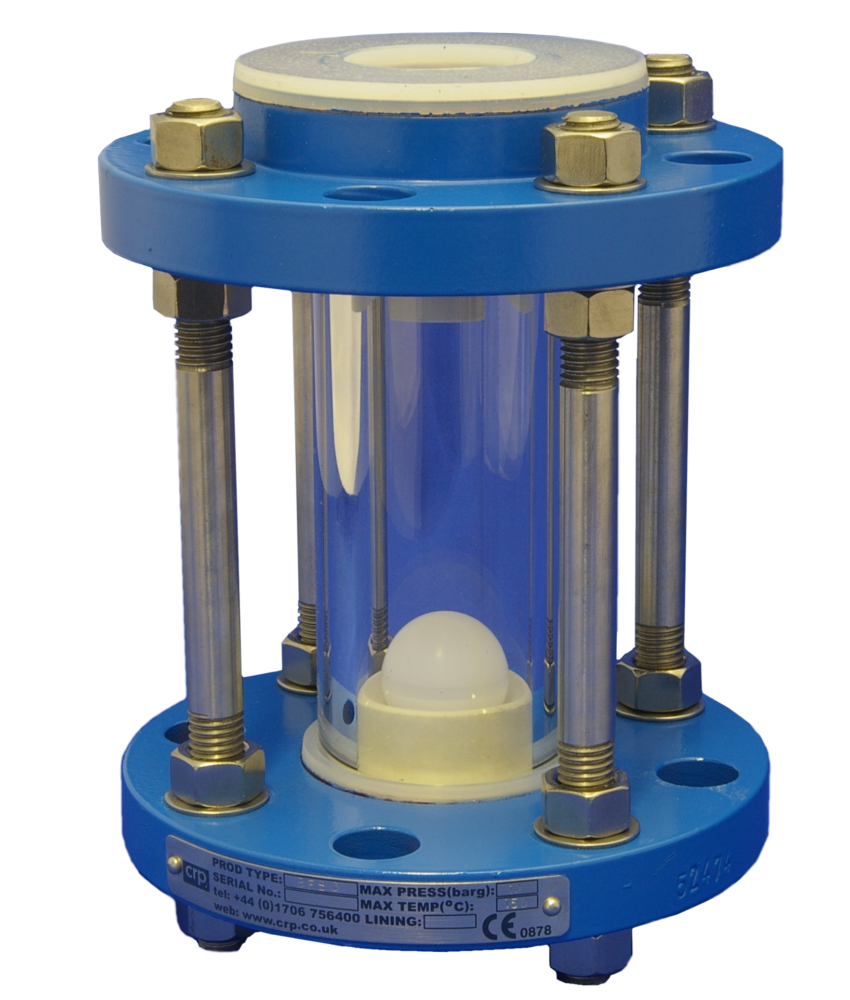
2. Extract Sample
By introducing site vacuum to the system the sample media is drawn up the dip pipe into the sight glass chamber, a hollow PTFE ball floats on the sample media giving both a clear level indication and acting as a non return valve prevent sample product travelling down the vacuum line. Once sufficient volume is held within the sight glass the vessel isolation valve is closed trapping the sample in the sight glass chamber.
3. Introduce some compressed purge gas.
A brief operation of the purge valve will add a little pressure to the sight glass section to aid in dispensing the sample from the sight glass into the bottle.
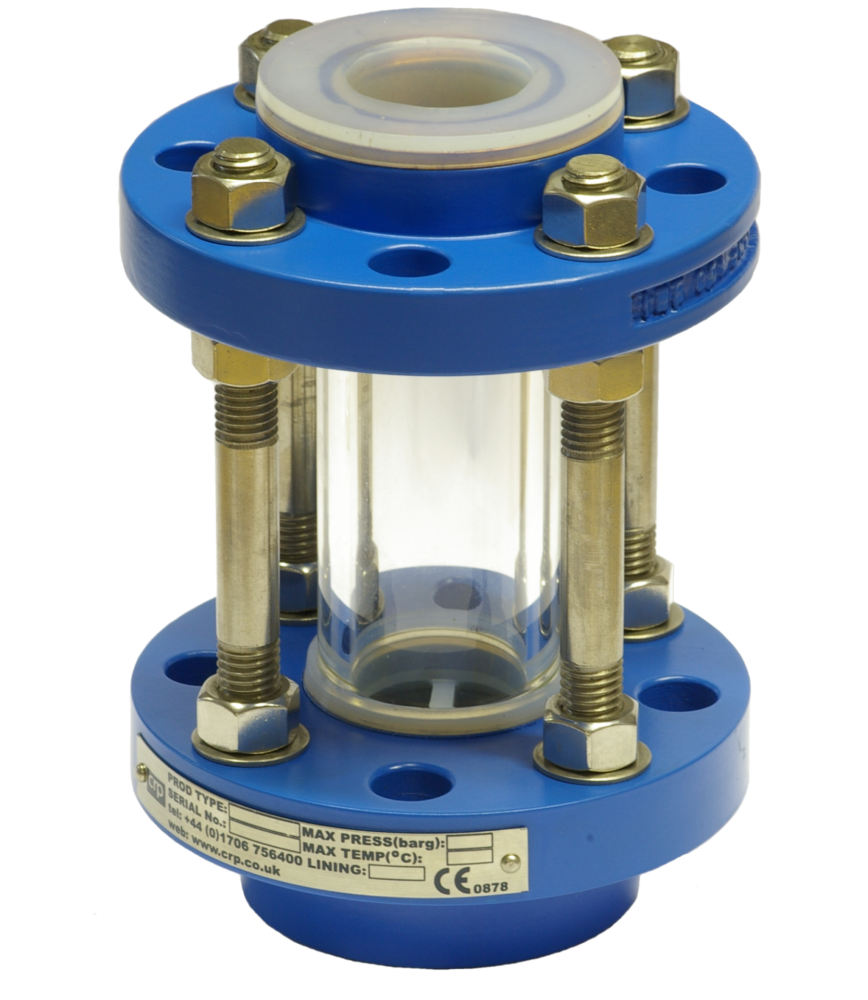
4. Dispense Sample
The sample is dispensed from the sight glass chamber into the sample bottle by opening the sample dispensing valve, letting the sample flow from the sight glass section into the sample bottle.
5. Final Purge
Finally the vessel isolation valve is opened and using nitrogen and or wash liquor the system and dip pipe are purged and cleaned clear.
Detailed operating instructions are supplied with all our sampling systems.
Please note, if the vessel is under pressure, then rather than using vacuum to draw the sample from a vessel we can vent the sight glass so the sample flows freely into the sight glass. We can also use an eductor to create vacuum in the sight glass chamber using compressed gas.