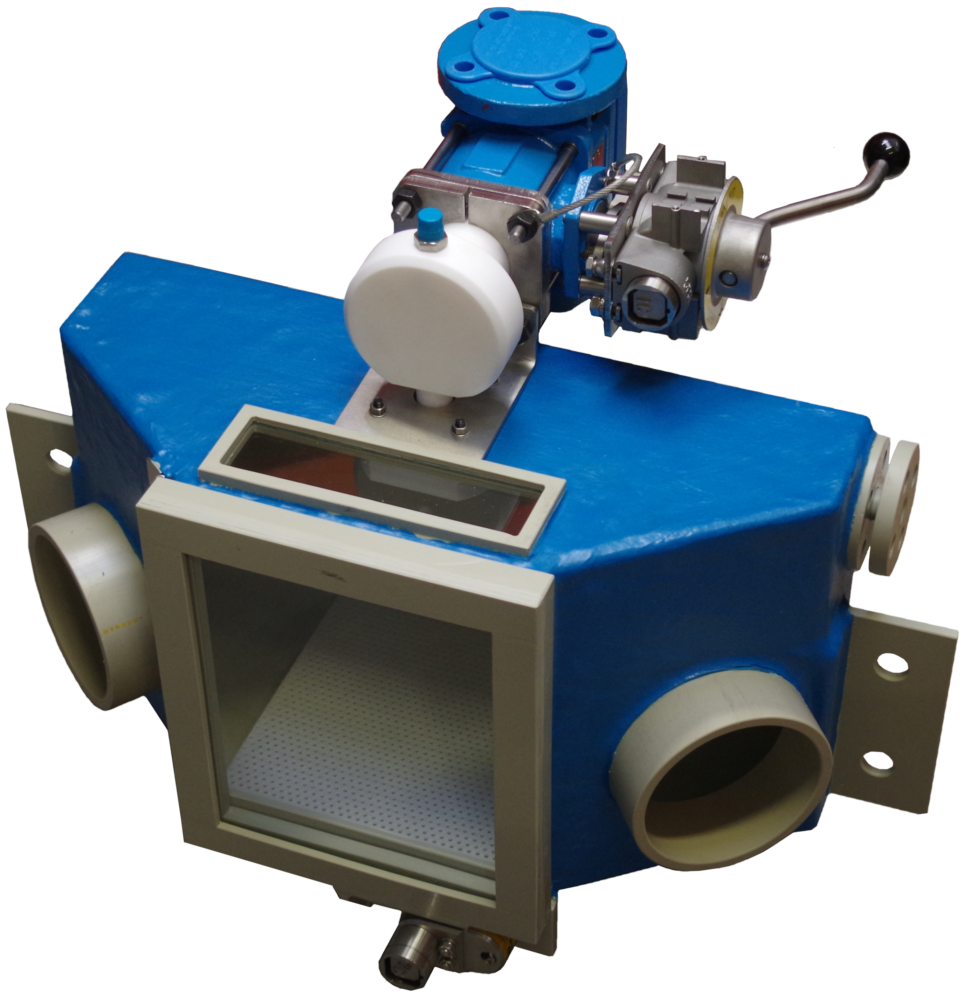
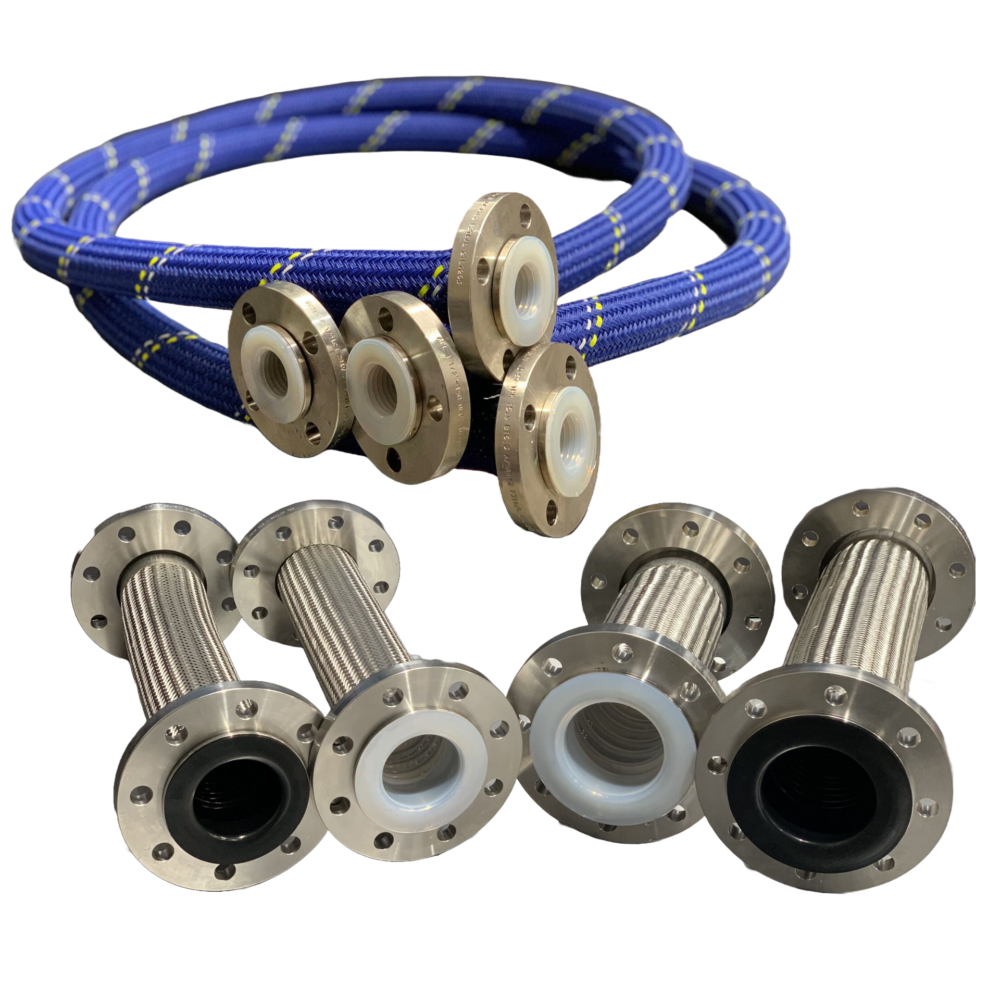
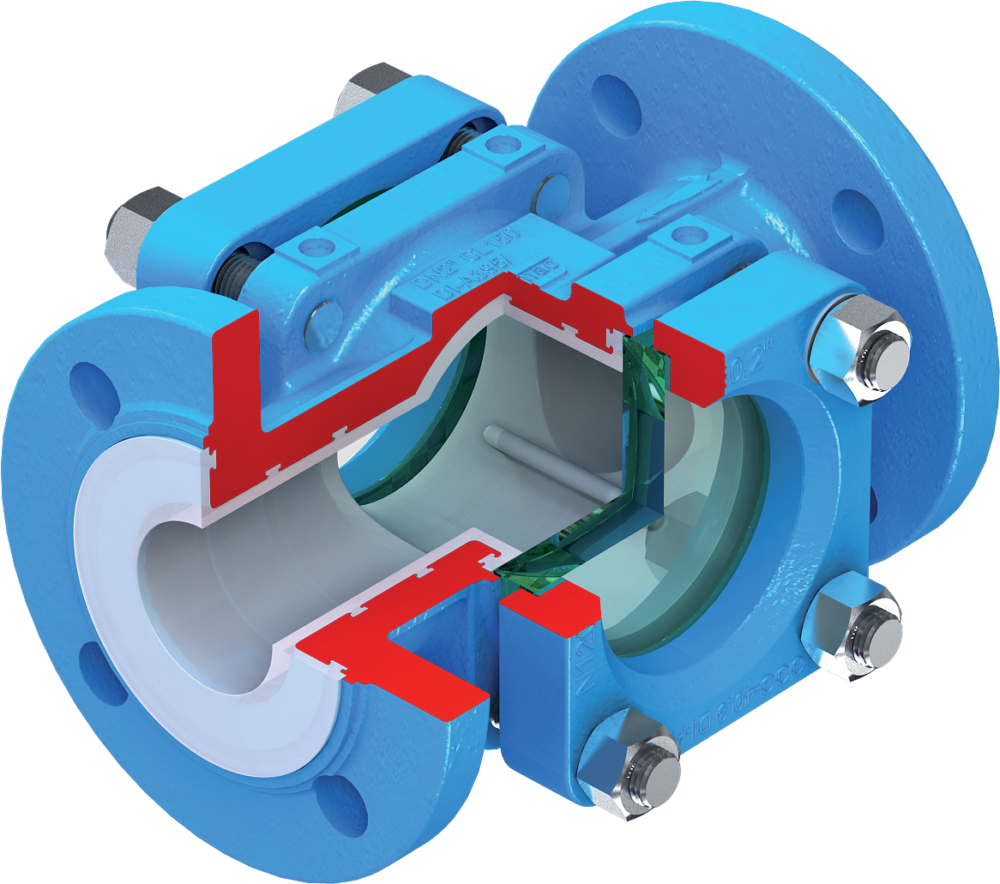
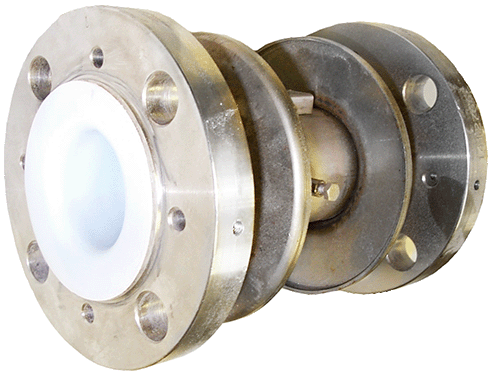
Key Processes
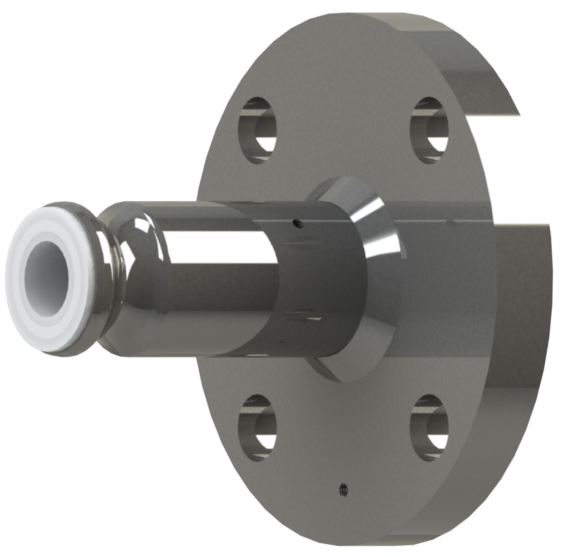
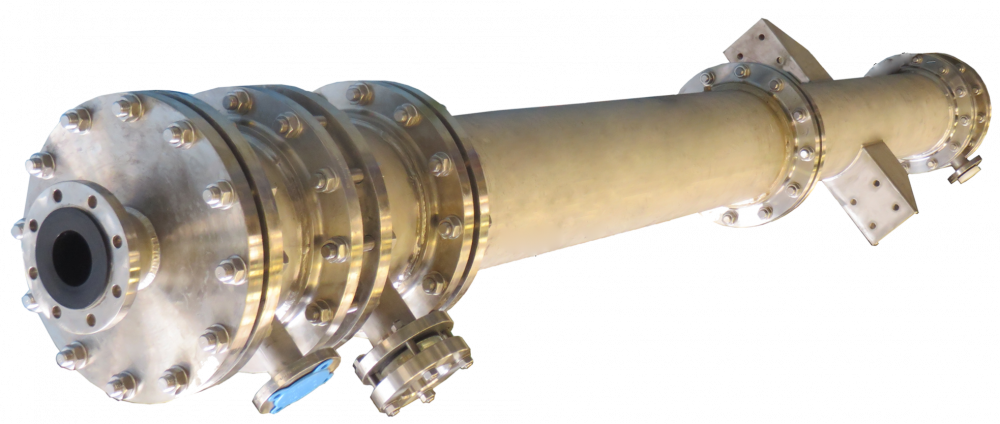
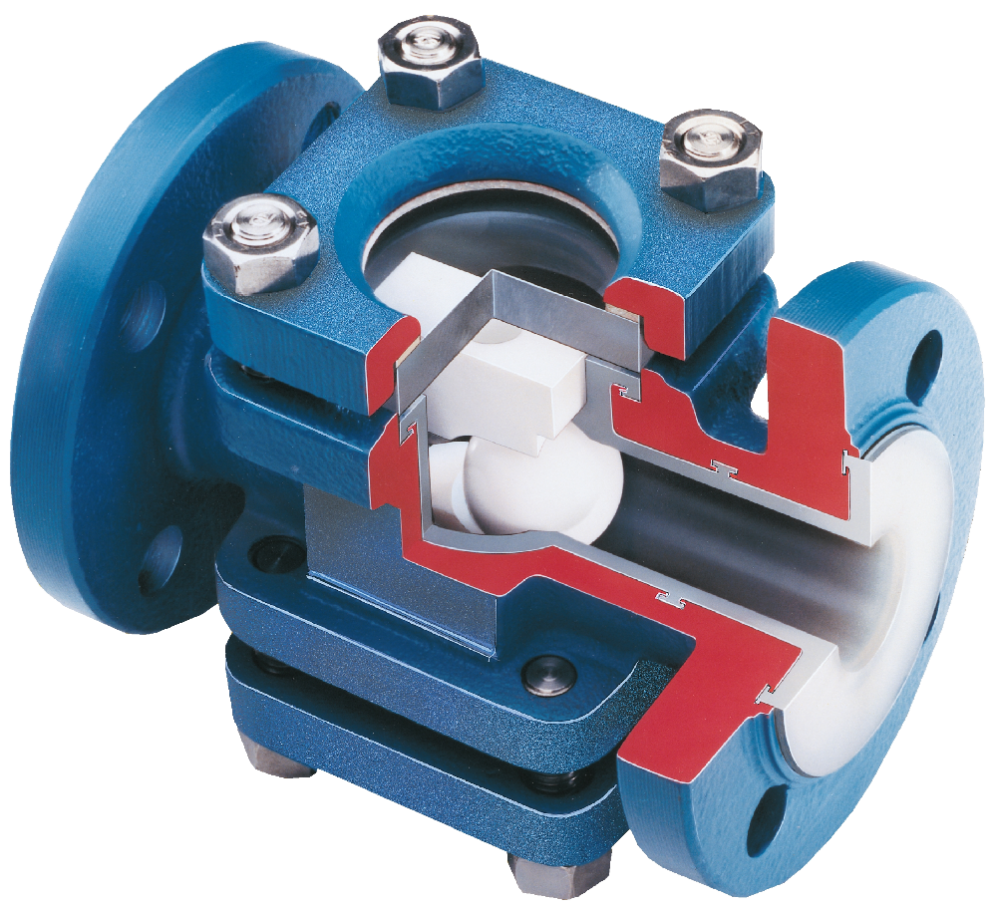
Our key manufacturing processes are the paste extrusion of PTFE pipe liners and their subsequent fitting into pipes and fittings or to produce bellows, and the moulding of fittings and other components using PFA.
Paste Extrusion
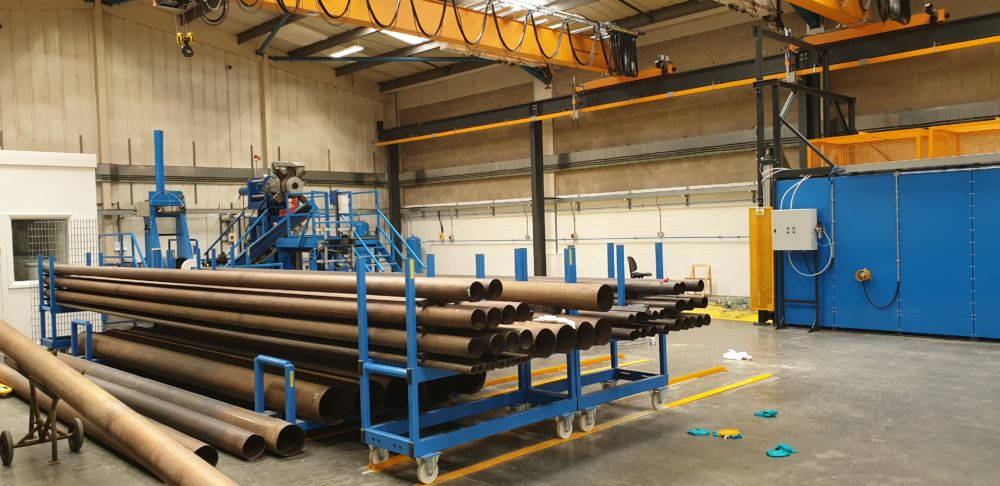
For paste extrusion CRP has a climate controlled blending plant for the cold conditioning of PTFE and its subsequent mixing with a hydrocarbon liquid which acts as a processing agent. After a period of at least 48 hours of warm conditioning the material is ready for extrusion.
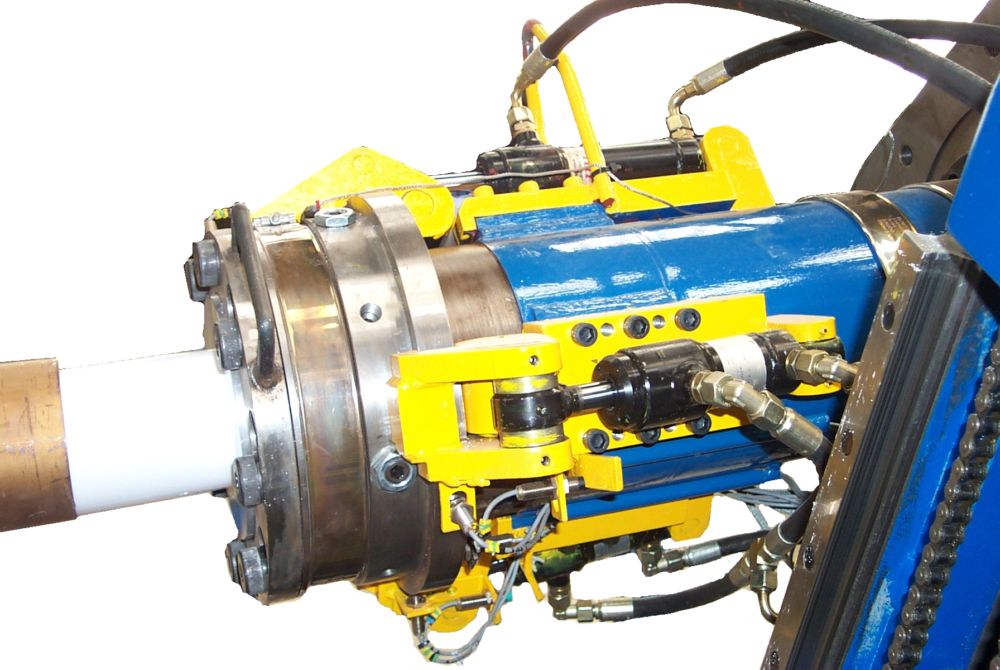
The first stage of paste extrusion is the manufacture of a billet weighing anything between 5 and 85kg. (11 and 187lb.) on a PLC controlled preform station. This soft waxy material is then transferred to the paste extruder and loaded into the barrel. Using polished aluminium tooling the PTFE is worked and extruded under great pressure into or over stainless steel support tubes. A number of lengths are extruded to complete a batch. These are then loaded into an oven for sintering. The sintering process takes 13 hours, after which the oven can be unloaded and the liners are ready for use – following materials testing.
CRP has two paste extrusion plants and associated ovens capable of producing liners from ½” to 14” (DN15 to DN350) in both virgin and static-dissipating PTFE resins.


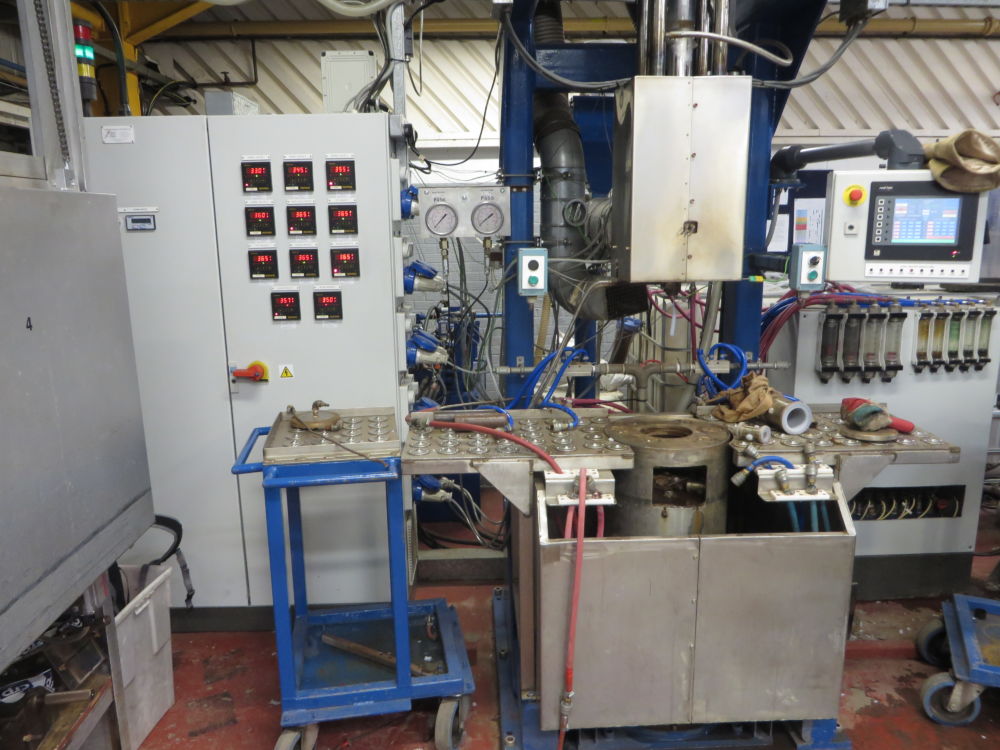
PFA Moulding
PFA is a melt processable fluoropolymer resin that provides all of the desirable properties of PTFE and more, whilst being capable of processing by conventional thermoplastic techniques. This includes transfer moulding – the process used by CRP.
Since high temperature chemical service is very demanding of any polymer, special high viscosity grades have been developed to maximise the performance of a lined component in both extreme harsh chemical and high/low temperature environments.
Because of the flow characteristics of these resins, high viscosity and very low critical shear rate, transfer moulding techniques conform best with such processing requirements.
Transfer moulding differs from injection moulding in that the mould temperature is above the melting point of the resin, also that the resin can be melted statically (in a melt pot) or dynamically in a plastification unit.
CRP has a number of transfer moulding machines, with both static and dynamic plastification units. The static plastification units are used for large sized components and one off specials, whilst the dynamic plastification units produce the higher volume and high precision components. The dynamic plastification units referred to colloquially as “screw-melt machines” are equipped with PLC controls enabling automated control of the complete moulding cycle, including mould filling, injection speed and pressure and all aspects of mould cooling.